 Image credit: ESPR
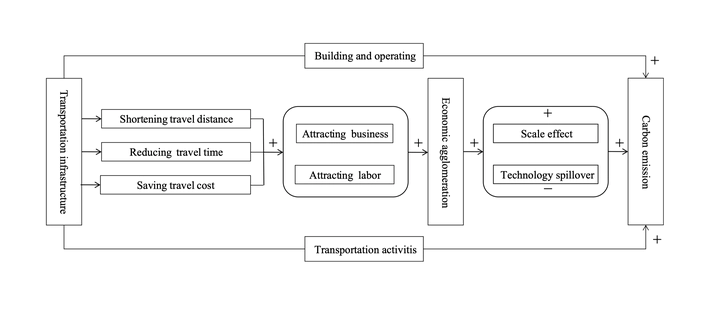
Image credit: ESPRAbstract: This study analyzes the effects of transportation infrastructure on carbon emissions (CE) based on the level of urban economic agglomeration. For this purpose, 281 Chinese cities are considered during the period 2003–2017. A Moran’s I is used to assess the spatial distribution characteristics of transportation infrastructure and CE. In addition, a spatial Durbin model is employed to explore the spatial spillover effect of transportation infrastructure on CE. Furthermore, economic agglomeration is considered as a crucial transmission mechanism. The empirical results show that (1) a significant spatial autocorrelation exists between transportation infrastructure and CE. (2) Transportation infrastructure significantly aggravates CE, with the “neighboring effect” being surprisingly more potent than the “local effect.” (3) Economic agglomeration is a valid transmission channel through which transportation infrastructure affects CE, the intensity of which varies with the level of economic agglomeration. Our recommendation is that policy-makers should pay attention to the development of local transportation, as well as their neighboring cities, and should accelerate the advancement of green transportation.